Generative AI is reshaping how marketers research, produce, and distribute content. Assistant value shows up only when it ties to measurable business outcomes and runs within clear guardrails.
Use this guide to define the role of AI marketing assistants, align them with KPIs, design an operating model, and implement workflows that accelerate content while protecting brand and compliance.
McKinsey estimates generative AI could add $2.6 to $4.4 trillion in annual economic value, with roughly 75 percent concentrated in customer operations, marketing, sales, software engineering, and research.
Google began rolling out AI Overviews to U.S. users in May 2024 and expects to reach over a billion people by year-end. Adobe Analytics reported traffic to U.S. retail sites from generative-AI sources rose 1,200 percent by February 2025, with 12 percent more pages per visit and 23 percent lower bounce rates than other traffic.
What Is an AI Marketing Assistant
An effective AI marketing assistant turns repeatable marketing tasks into structured, reusable workflows instead of one-off chatbot conversations.
An AI marketing assistant is a reusable workflow combining prompts, tools, and memory to complete a bounded marketing task with quality gates. It is not a single ad hoc chat session. You need to respect this difference to avoid treating assistants as magic chatbots rather than productized services.
Core terms matter here. An LLM is a large language model that generates or transforms text. RAG stands for retrieval-augmented generation that grounds the model with your documents. An agent is an autonomous tool-using assistant executing multi-step goals. HITL means human-in-the-loop checkpoints for review and approval.
Increasingly, specialised assistants such as an AI interview assistant help marketing teams streamline hiring workflows, conduct structured candidate assessments, and integrate recruitment insights into broader operational systems.
Assistant types map to common work patterns. On-demand copilots help with drafts and analysis when you prompt them. Event-driven automations trigger from CMS or CRM events automatically. Goal-oriented agents plan, research, draft, and QA to a defined acceptance criterion without constant supervision.
Design Principles for Useful Assistants
- Scope the job narrowly, such as drafting an SEO outline with citations and an internal link plan
- Give the assistant tool access for retrieval, analytics pulls, and CMS operations where appropriate
- Log all tool actions for transparency and debugging
- Enforce HITL checkpoints for facts, brand, legal, and deliverability before publishing
For example, a demand generation team might use an assistant scoped only to build SEO briefs from target keywords. It pulls top-ranking pages, extracts headings, suggests internal links, and outputs a draft outline for a marketer to refine.
The Business Case Leadership Cares About
Leaders back AI marketing assistants when they see direct impact on revenue, efficiency, and risk rather than experimental novelty.

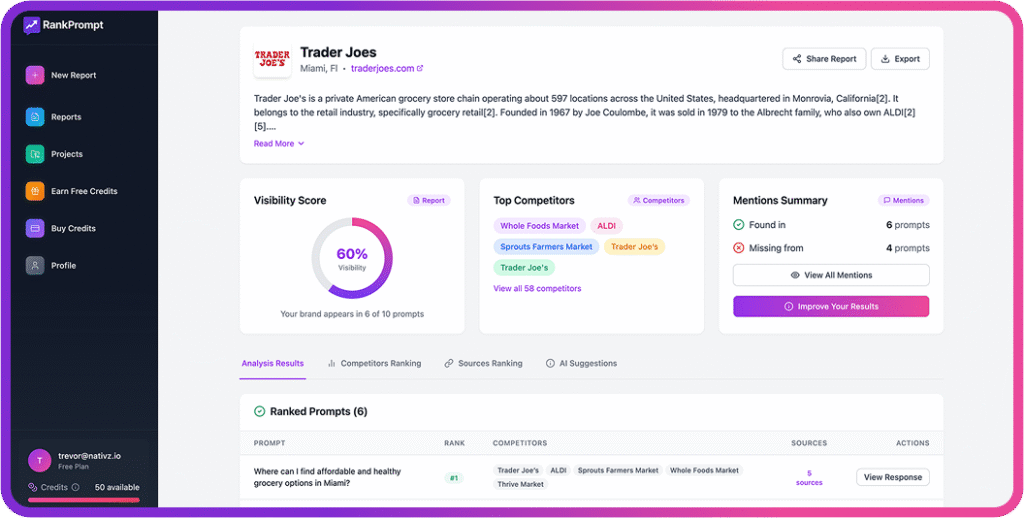
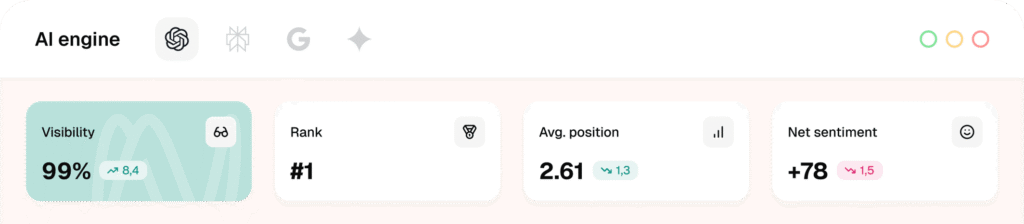
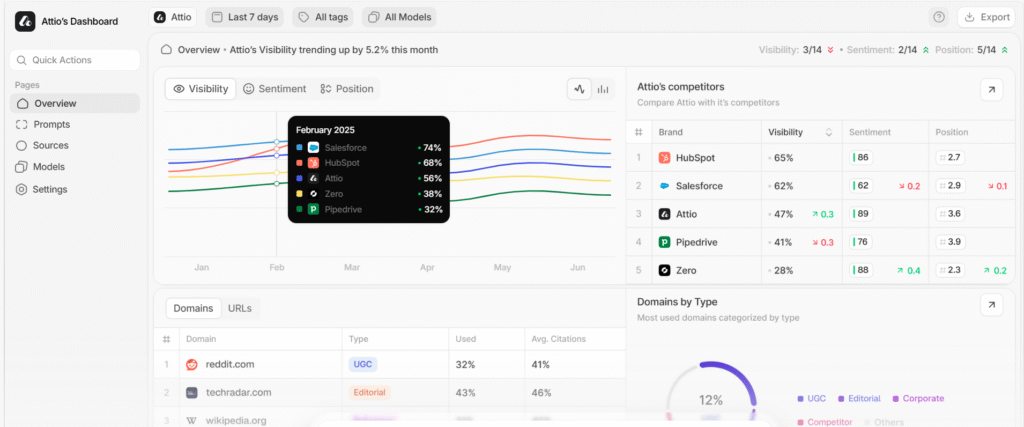
Tie assistants to KPIs your leadership already tracks to win budget and maintain support. These include content velocity measured in assets per week, SEO and AI visibility measured by rank plus inclusion in AI engines, MQL quality based on fit and intent, CAC and LTV ratios, and sales cycle time.
HubSpot reports marketers save approximately three hours per content asset and two and a half hours daily using generative AI. Salesforce finds 51 percent of marketers already use or test generative AI, expecting around five hours saved weekly, while accuracy and trust remain top concerns.
Here is a simple ROI model you can adapt. Calculate hours saved multiplied by loaded hourly rate, add incremental pipeline multiplied by close rate multiplied by average selling price, then subtract AI tooling costs plus QA time plus storage. Cost drivers to account for include model inference tokens, vector storage and retrieval, orchestration and monitoring, and SME review time.
Assistant Operating Model
A clear operating model turns AI assistants from side projects into reliable services that your marketing team can depend on every day.

Treat assistants like productized services with clear owners, SLAs, and change management rather than one-off experiments. This mindset shift separates teams that scale successfully from those whose pilots stall.
Define these roles clearly. A Product Owner from marketing ops manages the roadmap and SLA. A Prompt and Workflow Designer handles patterns and guardrails. An SME Reviewer ensures domain accuracy. A Data and Governance Lead manages sources, access, and compliance.
Cadence and Artifacts
- Weekly: run a retro with incident review covering hallucinations and policy flags, plus backlog triage
- Monthly: evaluate prompts versus quality KPIs, test alternative models and toolchains, refresh training examples
- Quarterly: conduct a roadmap review linking use cases to content velocity, GEO visibility, MQL quality, and revenue assists
Data Foundations and Brand Safety
Strong data foundations and brand controls keep assistants from hallucinating, going off-voice, or putting your compliance posture at risk.

Great assistants rely on a curated brand brain that grounds every output in accurate, approved information. This foundation prevents hallucinations and ensures consistency across channels and campaigns.
Your brand brain should include product sheets, personas, voice and style guides, a claims library with citations, compliance lists of what to avoid, approved examples, and competitive intelligence. Build a retrieval index with metadata covering topic, funnel stage, last updated date, owner, citations, and risk flags.
Brand and Compliance Controls
- Maintain an authoritative claims library with evidence sources and expiration dates
- Require claims IDs in all outbound content
- Create refusal rules for regulated content and auto-escalation to legal when triggered
- Log all assistant decisions and preserve inputs and outputs for audit
As regulations evolve, your governance lead can update refusal rules and claims in one place so that every assistant, and every supporting Wing Assistant marketing specialist, automatically inherits the latest standards.
Core Workflow Pattern
A consistent pipeline across use cases makes AI outputs predictable, reviewable, and easier to measure against quality benchmarks.
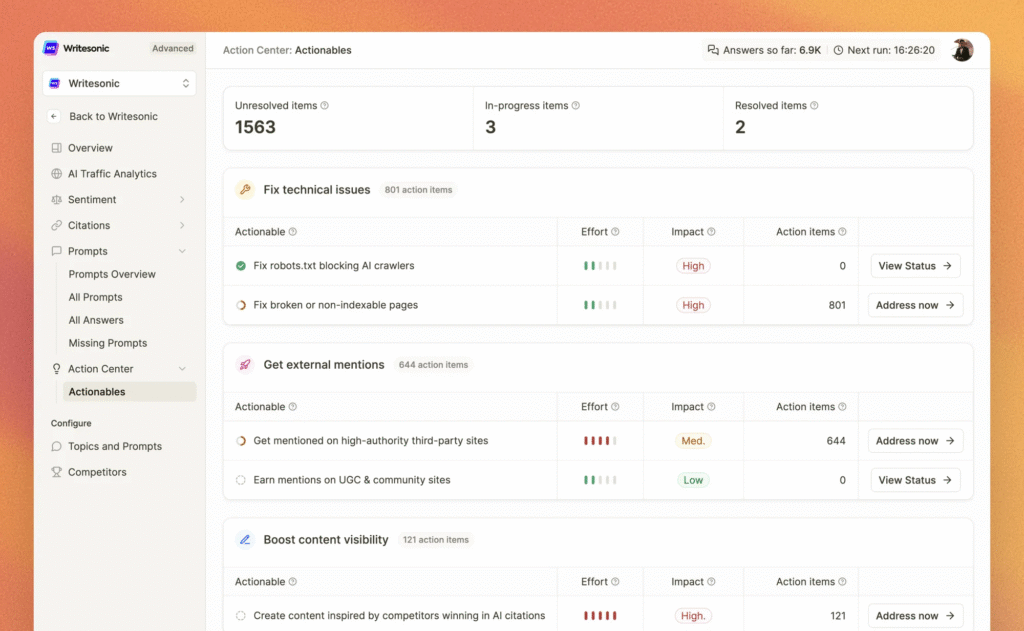
Follow a six-stage pipeline that is reused across use cases to ensure predictable quality. The stages are Intake, Draft, Enrich, QA, Publish, and Measure. This pattern works whether you are producing blog posts, emails, or ad copy.
Your intake template should capture goal, audience, channel, CTA, KPIs, constraints including claims and compliance flags, must-use sources, internal links, and deadlines. Measure with dashboards that track cycle time, errors by type, inclusion in AI engines, organic and referral lifts, and outcome metrics like MQLs and pipeline.
Use Cases by Funnel Stage
Focusing on a small set of high-impact use cases builds quick wins and creates proof points you can reuse across the organization.
Start with three to five use cases where assistants can save time and improve outcomes, then measure against baselines and a control group. Prioritize based on time savings potential and strategic importance to pipeline and retention.
Pick at least one use case in each stage of the funnel, such as top-of-funnel research, mid-funnel nurture content, and bottom-of-funnel sales enablement assets. That spread helps stakeholders see value across the journey instead of viewing AI as a niche SEO experiment.
Research and Analysis
Assistants excel at audience synthesis from CRM notes and surveys, competitor page and messaging comparisons, and SERP and AI snippet audits. Deliverables include insight briefs with citations, gap analyses, and prioritized question clusters.
Content Production
Assistant-generated outlines, first drafts, and repurposed assets work well when you enforce acceptance criteria. Require claim IDs to be present, quotes to be attributed, and schema suggestions to be included in every deliverable.
SEO Accelerators
Internal linking suggestions by topic cluster, schema generation for FAQ and HowTo markup, and FAQ expansion for snippet inclusion all deliver measurable results. Output must include target intents, evidence snippets, and anchor placement notes.
GEO in Practice
Generative Engine Optimization positions your content so AI systems can confidently quote, cite, and recommend your brand in their synthesized answers.
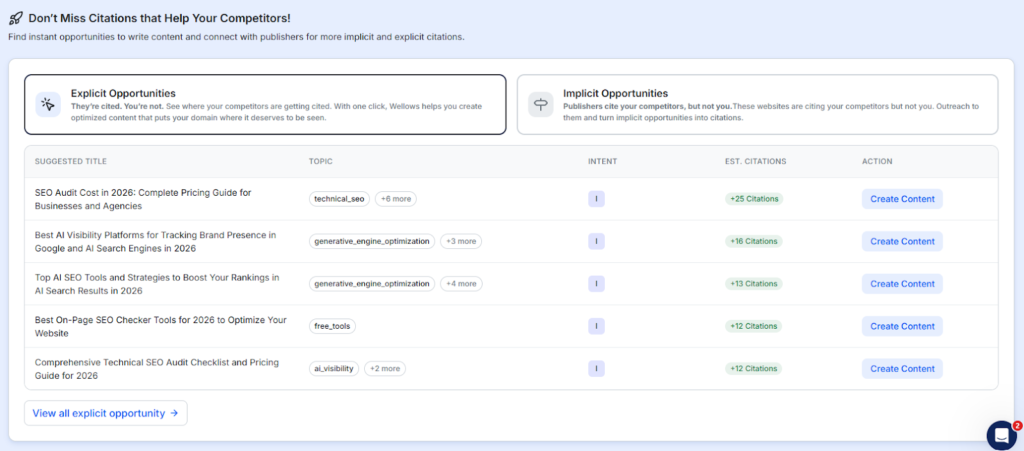
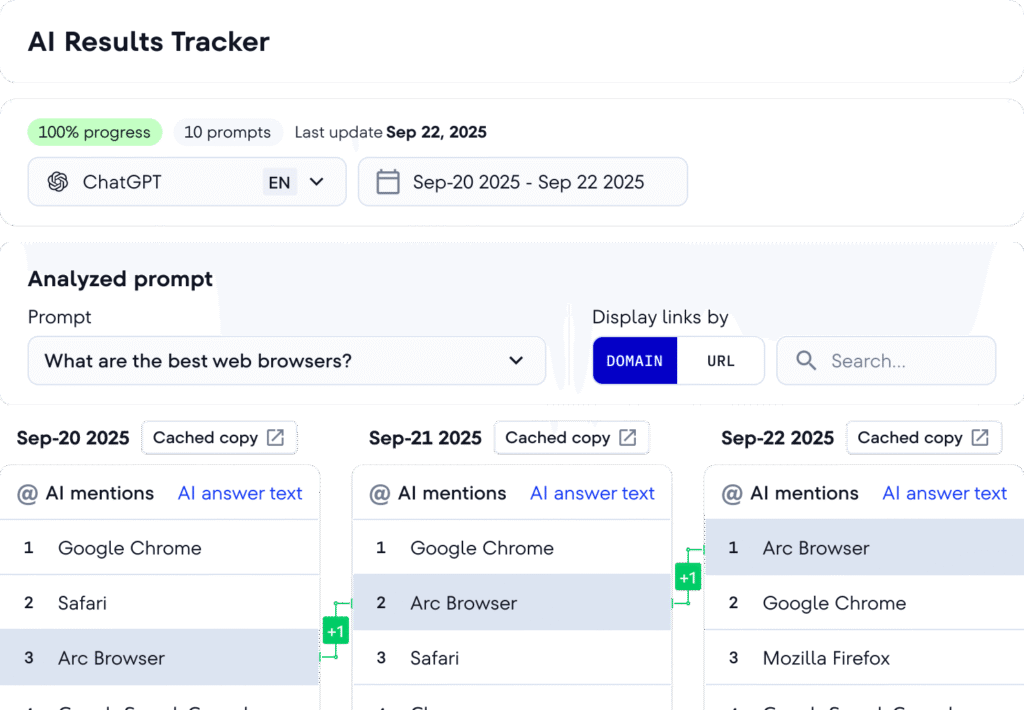
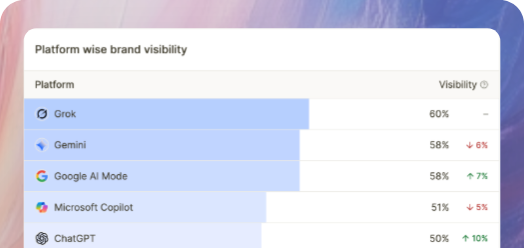
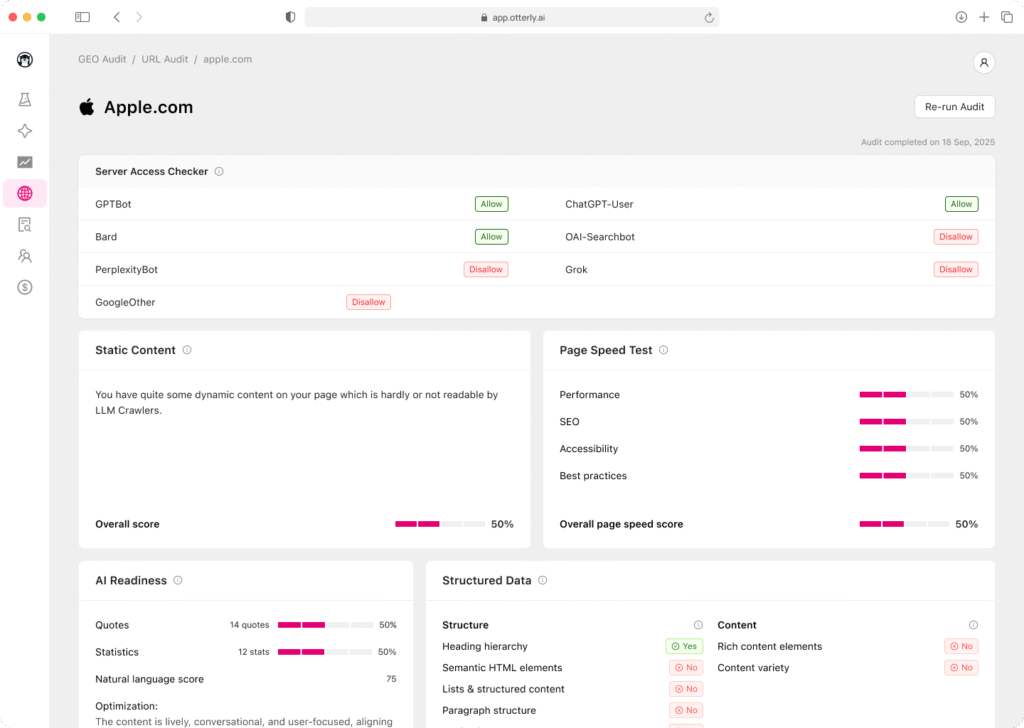
Generative Engine Optimization positions your brand to be included, cited, and recommended in AI systems and Google Overviews. This emerging discipline requires specific content patterns and measurement approaches.
Identify assistant-friendly questions covering how, why, and comparison topics. Build concise, citation-backed answer pages that engines can ingest. Google reports that Overview links can attract more clicks than traditional blue links for covered queries.
Page Patterns That Win Inclusion
- Concise answers of 40 to 120 words placed high on the page with citations and expandable depth below
- Schema and anchor linking to related FAQs and How-tos
- Author bios with credentials and revision dates
- Clear product and credibility markers including feature tables and customer quotes
Email Deliverability Guardrails
AI-generated emails need strict deliverability controls so speed gains never come at the cost of sender reputation or compliance.

Assistants must never ship non-compliant emails, and deliverability must be protected by default. Enforce Gmail bulk sender requirements including SPF and DKIM authentication, DMARC alignment, one-click unsubscribe for promotional emails, and keeping spam rates under 0.3 percent.
Add pre-send QA covering seed testing across inbox providers, broken link checks, brand voice compliance, accurate headers and footers, and list hygiene rules. Implement a do-not-send circuit breaker when complaint rates spike or domain reputation dips.
Build Versus Buy Versus Hybrid
Choosing between building, buying, or mixing approaches depends on your risk tolerance, internal skills, and how fast you need measurable impact.
Build when you have strict data constraints, security needs, and engineering capacity to maintain orchestration. Buy when speed to value, governance tooling, and support matter more. Choose hybrid when you want to customize orchestration but use off-the-shelf components.
Cost out inference, storage, orchestration, and QA headcount for each path. Plan SLAs for latency, uptime, and review turnaround. Consider that MIT Project NANDA reports roughly 95 percent of enterprise pilots had no measurable profit and loss impact due to integration and workflow gaps.
When to Augment with Human Capacity
Typical triggers include quality dips in fact-checking during launches, prospecting backlogs, or multi-locale content requiring fast adaptation. Core reviewers should handle claims and brand while flex capacity executes repeatable tasks alongside AI workflows.
When launches compress timelines and QA backlogs emerge, many teams pair their assistant with additional human capacity to handle repeatable QA, research, and prospecting tasks so editors can focus on approvals and campaign strategy. Instead of hiring full-time headcount immediately, they often tap an external partner such as Wing Assistant, using a virtual marketing assistant to execute structured checklists, monitor outputs across channels, and surface issues for marketing leaders to address. This pattern preserves quality and speed without burning out your core team.
Thirty-Sixty-Ninety Day Rollout Plan
A structured 90-day rollout proves value fast while building the governance, training, and measurement practices you need for scale.
A pragmatic twelve-week plan demonstrates value quickly while building governance and measurement muscle. Start lean and expand based on evidence.
Days zero to thirty: baseline metrics, pick two use cases, define prompts, connect data sources, set QA gates, secure email deliverability controls, and define GEO hypotheses. Days 31 to 60: pilot with assistant versus control, fix failure modes, enrich the brand brain, add GEO checks, and start AI visibility tracking. Days 61 to 90: scale to a third use case, publish an internal playbook, instrument dashboards, and present ROI versus baselines.
Common Failure Modes
Most AI marketing failures trace back to vague scopes, weak governance, or treating assistants as side projects instead of core workflows.
Frequent failure modes include poor workflow integration with no CMS or CRM hooks, weak governance with no claims library or QA gates, and chasing novelty over KPIs. Design your operating model to avoid these traps from day one.
Fixes include narrowing the job to be done, integrating assistants with existing systems, adding HITL review, training teams on prompts and brand safety, and retiring low-impact use cases after timeboxed tests. If QA becomes the bottleneck, add flex human capacity or reduce scope rather than compromising quality.
Conclusion
Effective AI marketing programs treat assistants as governed, measurable services that pair automation with the right level of human oversight.
AI marketing assistants deliver durable value only when they are embedded in operations, governed by clear rules, and measured against business KPIs. Start with two scoped use cases, stand up governance and deliverability guardrails, and track AI visibility alongside organic and pipeline metrics. Teams that invest in GEO-ready content, robust QA, the right blend of automation and Wing Assistant human support, and disciplined measurement will capture outsized gains as discovery shifts toward generative engines.