Free Website Speed Checker
Instantly Test How Fast Your Website Loads
Enter your website URL to see how fast your site loads around the world and learn what might be slowing your site down- No signup required!
How it Works
1. Enter your website URL
Type your website URL in our tool above, then click “Submit”. You can test any page – your homepage, blog posts, or product pages.
2. Select Location
Choose which region to test from the drop-down menu. It could be Tokyo, Frankfurt, London, Washington D.C., San Francisco, Sydney, or São Paulo. Then click “Test”.
3. Get Instant Speed Results
Our tool will measure your page load time, performance score, page size, and number of requests. You’ll see exactly what’s loading on your page and how fast it performs.
Why use Click Raven’s Free Website Checker?
✔ It’s Free. No Signup Required – Test your website speed instantly without creating an account or entering payment information.
✔ Unlimited Free Tests – Run as many tests as needed without hitting usage limits.
✔ Test from Multiple Global Locations – Choose from 7 locations: Tokyo, Frankfurt, London, Washington D.C., San Francisco, Sydney, and São Paulo.
✔ Comprehensive Speed Analysis – Get your performance score, exact load time in milliseconds, total page size, and request count in one view.
✔ User-Friendly Interface– Designed for ease, our tool offers a straightforward process for your speed test.
✔ Detailed Content Breakdown – See which content types (images, scripts, stylesheets) consume the most bandwidth and slow down your site.
✔ Response Code Monitoring – Identify any failed requests, redirects, or errors affecting your site’s performance.
More than just a Website Checker
Click Raven offers a powerful suite of free SEO tools to help you improve website performance and search visibility. Here are some additional tools:
✔ Google Rank Checker – Check where your website ranks on Google for any keyword instantly.
✔ Keyword Research Tool – Find new keywords to boost your search visibility completely free.
✔ Meta Tags Extractor– Extract meta tags from any website to analyze titles, descriptions, and other metadata.
✔ Crawlability Checker– Check if search engines can access your website and check your robots.txt file.
✔ Bad Links Checker– Find and fix broken links that hurt user experience and search rankings.
The Ultimate Guide for Improving Your Website’s Speed
A slow website could cost you visitors, customers, and search rankings. That’s why it’s essential to test website speed regularly using a reliable page speed checker. Our free tool helps you check website speed from multiple global locations so you know exactly how fast your site loads for visitors worldwide.
When someone clicks on your site and waits more than three seconds, they often leave and seek faster alternatives.
This shows that speed isn’t just a technical detail. It directly impacts your success. Fast sites keep visitors engaged, rank higher in Google, and turn more visitors into customers. On the other hand, slow websites frustrate users and could damage your brand.
Let’s show you how to identify what’s slowing your site down and how to fix it.
What is Website Speed?
Website speed refers to how long your page takes to fully load and become usable. When you run a website speed test, you measure this loading time with other performance metrics. A good page speed checker, like Click Raven, helps you understand these metrics through an easy-to-read website performance test report.
Website speed is measured from when a user clicks your link until everything appears and they can interact with your content.
How is Website Speed Measured?
When you check website speed using Click Raven’s free speed test tool, you’ll see several key metrics:
- Load Time: The total time it takes for your page to completely load. Shown in milliseconds (aim for under 3,000ms)
- Performance Score – Many website speed checkers combine multiple measurements into a single score from 0-100%.
- Time to First Byte (TTFB) – This shows how quickly your web server responds when someone requests your page. It can be viewed as your server’s reaction time. A lower TTFB means a quicker response from the server.
- First Contentful Paint (FCP) – This is the time it takes for the first piece of content to appear on the screen. Faster FCP improves the perception of speed.
- Page Size – The total amount of data downloaded to display your page. Smaller is better. Most pages should be under 2-3 MB. Large page sizes mean slower loading, especially on mobile networks.
- Number of Requests – The number of separate files your browser needs to download. Fewer requests generally mean faster loading. Most sites should aim for under 50 requests per page.
Importance of Website Speed
Website speed is a crucial factor that directly affects three critical areas: user experience, conversion rates, and search engine rankings.
1. Impact on User Experience
When you run a website loading speed test, you quickly discover how user experience suffers from slow sites. Research shows that 47% of users expect a page to load in two seconds or less. If your site takes longer, users may abandon it.
Key aspects of user experience include:
- Frustration Levels – Slow sites frustrate visitors. They’re more likely to abandon your site and find what they need elsewhere.
- Session Duration – Fast sites encourage people to stay longer and view more pages.
- Accessibility – A good speed ensures your content is accessible to a broader audience. Mobile users on slower connections need fast-loading sites. If your pages are heavy, you’re excluding potential visitors.
2. Effect on Conversion Rates
Website speed directly impacts your conversion rates. Studies show that even a one-second delay can result in a significant drop in conversions.
Research from major retailers has shown that improving load time can significantly increase conversions and revenue.
E-commerce sites are especially sensitive to speed issues. How?
- Add to Cart: Slower sites can cause abandoned shopping carts, causing lost revenue.
- Form Submissions: Slow forms can lead to incomplete signups and missed opportunities.
- Bounce Rates: Faster-loading pages reduce bounce rates, keeping potential customers engaged.
3. Influence on Search Rankings
Search engines like Google use website speed as a ranking factor. Faster sites rank higher in search results, especially on mobile.
Key factors include:
- Crawl Efficiency: Search engines crawl fewer pages when your site loads slowly. This means new content takes longer to appear in the search results.
- User Engagement Metrics: High bounce rates from slow speeds signal poor quality to Google, and over time, this can negatively affect your rankings and visibility.
Tip: Use Click Raven’s Google Rank Checker to monitor how speed improvements affect your rankings.
Factors That Affect Loading Speed
Website loading speed is influenced by various elements that can significantly impact user experience. Understanding these factors will help you optimize your site more effectively.
1. Web Hosting Quality
Your hosting provider directly affects your site’s speed. Therefore, you need a high-quality hosting provider for faster servers and better uptime.
Consider the type of hosting you select: shared, VPS, or dedicated.
- Budget Shared hosting can lead to slower speeds because you share resources with many other websites.
- VPS (Virtual Private Server) means more resources are dedicated to your site.
- Dedicated hosting means it’s your own server and thus provides more control and reliability.
- Managed WordPress hosting: Specifically optimized for WordPress sites.
Server location matters too. Choose a hosting provider with servers near your main audience. If most of your visitors are in Europe, hosting in Frankfurt will be faster than hosting in Sydney.
2. Resource-Heavy Content
Images, videos, and other multimedia elements can slow your site significantly if not optimized. A single uncompressed photo can take longer to load than your entire page should.
Since large files take longer to load, compress images before uploading them. Use formats like JPEG for photos and PNG for graphics with text. WebP is newer and compresses even better.
For videos, use MP4 to reduce size without losing quality, but also consider hosting on YouTube or Vimeo instead of your server. These platforms handle compression and streaming automatically, significantly improving your loading times.
3. Excessive HTTP Requests
Every element on your page, from images to scripts, requires a separate HTTP request. More requests mean slower page loading.
You can reduce these requests by:
- Combining multiple CSS files into one
- Combining JavaScript files where possible
- Using CSS sprites for multiple small icons
- Removing unnecessary plugins and scripts
Aim for fewer than 50 requests per page if possible.
4. Browser Caching
Browser caching stores parts of your website on visitors’ devices so they don’t need to download everything again on repeat visits.
Enable caching through your hosting provider or use a caching plugin if you’re using WordPress. This dramatically improves speed for returning visitors.
5. Third-Party Services and Scripts
Third-party services like ads, social media plugins, chat widgets, and analytics tools can significantly slow your site. Each service often requires separate HTTP requests that can slow down your site.
Evaluate the necessity of each third-party script and remove non-essential services to significantly expedite load times. Load necessary scripts asynchronously so they don’t block your main content from displaying.
How to Check Website Speed: Top Tools
A regular website speed test helps you spot problems before they affect your traffic.
Several free speed test tools offer insights into your website’s performance. They include:
1. Click Raven’s Free Website Speed Checker (Recommended)
Click Raven’s speed checker is the easiest way to test your website speed. Here’s how to use it:
Step 1: Enter Your Website URL
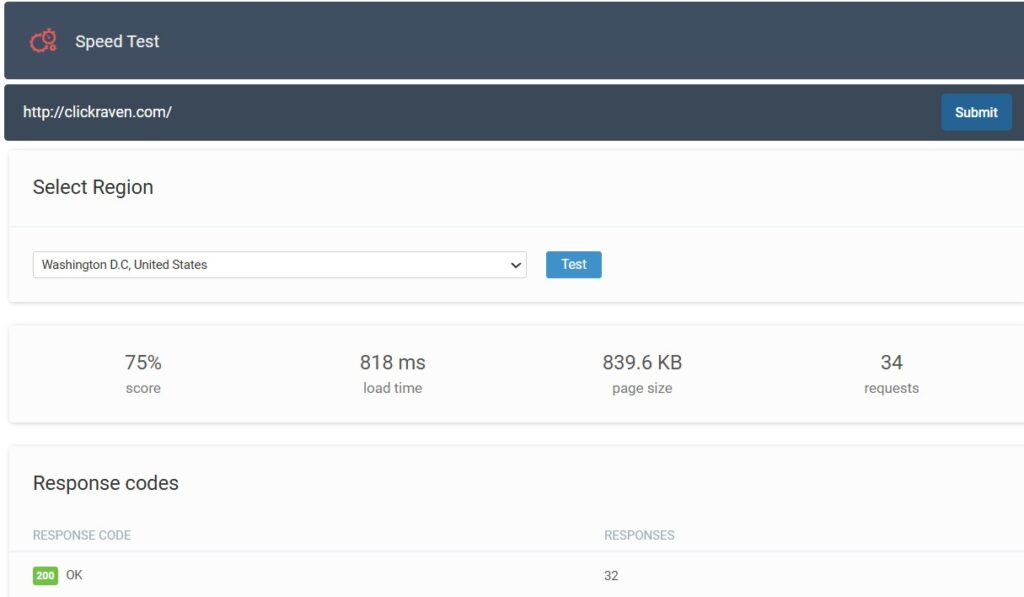
Go to Click Raven’s Website Speed Checker, type your complete website URL in the input field, and then click Submit.
For illustration purposes, we will use The Verge.

Step 2: Select Your Test Location
Choose which region to test from by clicking the dropdown menu.
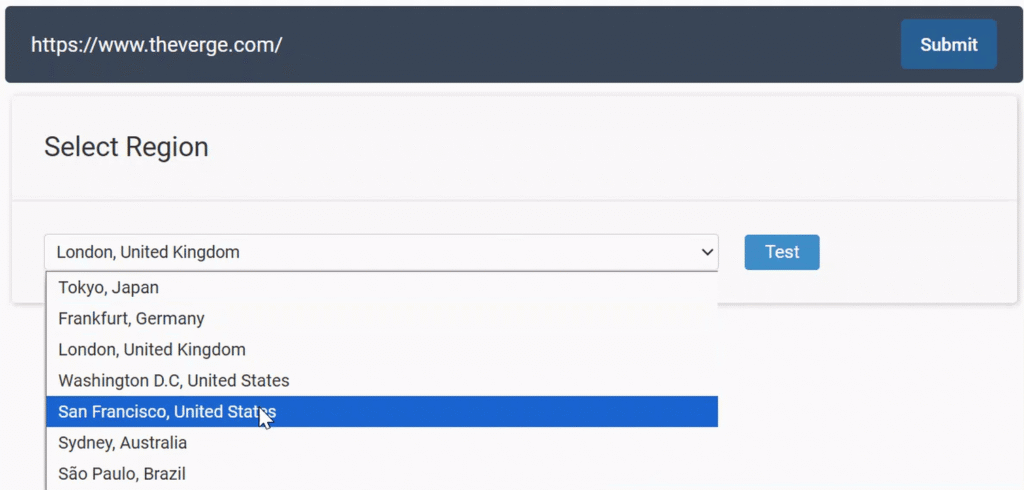
For the most accurate results, choose the location closest to where most of your visitors are located.
Step 3: Click “Test.”
Click the “Test” button and wait a few seconds while the tool analyzes your page.
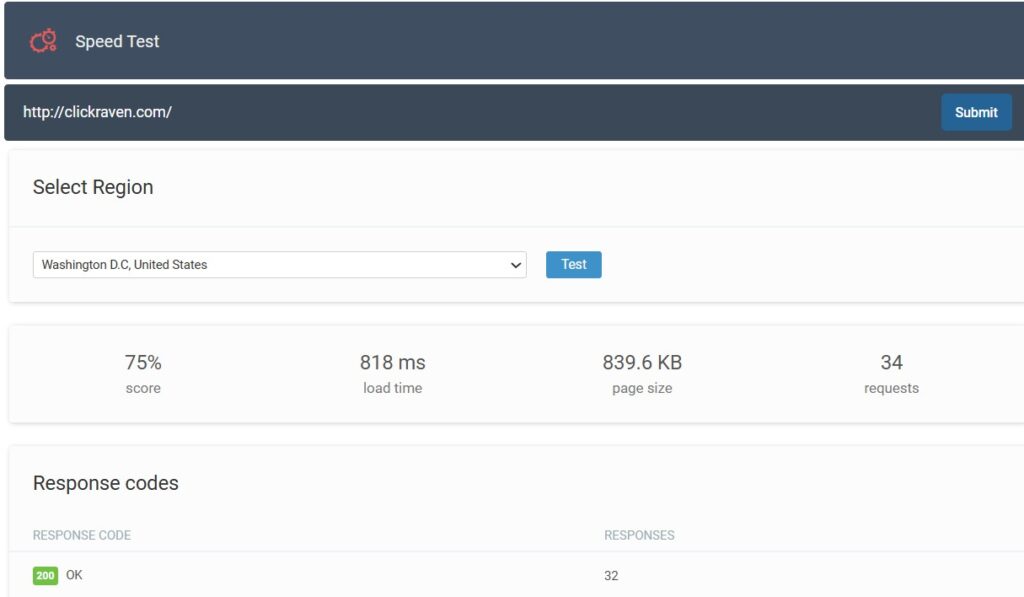
When you test with Click Raven’s free website speed checker, you’ll immediately see:
- A performance score (0-100%) showing overall website speed
- Load time in milliseconds
- Page size showing total data downloaded
- Number of requests your page makes
There will also be a detailed breakdown with:
- Response codes: Which files loaded successfully and which failed.
- Content size breakdown: What types of files use the most bandwidth?
- Content requests: How many requests does each file type require?
These are The Verge’s Click Raven test results from London, UK.
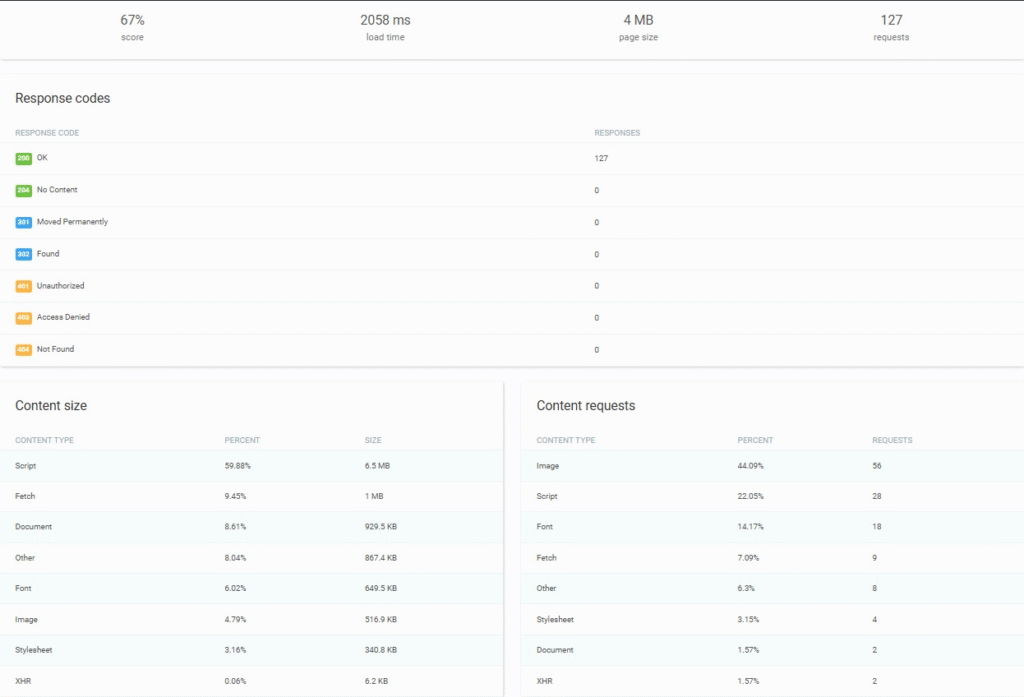
Use the insights from your speed test to optimize your site’s problems. After making changes, test your site again to confirm the improvements.
Understanding Your Click Raven Speed Test Results
After testing your website, you’ll see several key metrics:
1. Performance Score (0-100%)
Your overall speed score. Higher is better.
- 80-100%: Excellent – your site loads fast
- 60-79%: Good – minor improvements needed
- 40-59%: Poor – optimization required
- Below 40%: Critical – immediate action needed
2. Load Time (in milliseconds)
- Under 1,000ms (1 second): Exceptional
- 1,000-3,000ms (1-3 seconds): Good
- 3,000-5,000ms (3-5 seconds): Needs improvement
- Over 5,000ms (5+ seconds): Critical issue
3. Response Codes Breakdown
Your test shows which files loaded successfully:
- 200 OK: Files loaded correctly (good)
- 301/302: Redirects (too many can slow your site)
- 404 Not Found: Broken links (fix immediately)
- 403/401: Permission errors (needs fixing)
Tip: Use Click Raven’s Bad Links Checker to identify and fix the broken links.
4. Content Size Breakdown
Shows what’s using the most bandwidth:
- If Scripts are over 50%: Remove unnecessary JavaScript
- If Images are over 40%: Compress your images
- If Stylesheets are large: Minify your CSS
5. Content Requests
- Under 30 requests: Excellent
- 30-50 requests: Good
- 50-75 requests: Consider optimization
- Over 75 requests: Too many – combine files
Other Free Website Speed Checkers
2. Google PageSpeed Insights
Google PageSpeed Insights provides a detailed analysis of your website’s performance directly from Google. It scores your site on a scale from 0 to 100 on mobile and desktop, showing precisely what Google sees.
This website speed checker includes specific suggestions like “reduce unused JavaScript” or “properly size images.” These recommendations come directly from Google’s ranking algorithm.
Tip: Use this tool alongside Click Raven’s checker for the most complete picture of your site’s performance.
Additionally, it integrates seamlessly with Google Analytics for ongoing monitoring. Use it to ensure consistent performance, and periodically check and track your website’s speed over time.
3. GTmetrix
GTmetrix combines multiple testing methods and provides detailed waterfall charts showing exactly when each element loads. This visual timeline helps identify bottlenecks that need attention.
It combines Google’s Lighthouse and Web Vitals scores with its own analysis.
In addition, this tool tracks your site’s performance over time and can alert you if speed degrades. Free accounts allow regular monitoring of your site.
4. Pingdom Website Speed Test
Pingdom Website Speed Checker offers testing from multiple global locations and provides clear performance grades. The tool is particularly useful for tracking uptime alongside speed.
Pingdom’s interface is beginner-friendly with simple explanations of each metric. It’s a good alternative if you want a second opinion on your speed.
Why Test from Multiple Locations?
Your website’s speed varies depending on where visitors are located. A website that loads quickly in San Francisco might be slow in Tokyo.
The further your visitors are from your web server, the longer it takes for data to travel. This is called latency. Using your free website checker from multiple locations shows you the real experience of your global audience.
Choose your test locations based on where your visitors are:
- US audience? Test from Washington, D.C. or San Francisco.
- European visitors? Use London or Frankfurt.
- Asian traffic? Try Tokyo
- Australian users? Test from Sydney
- South American audience? Choose São Paulo
Optimizing Content for Speed
After you test website speed and identify issues, it’s time to optimize. Your load time checker results from Click Raven show which content types consume the most bandwidth. Use these insights to prioritize your optimization efforts.
1. Image and Video Compression
Large images and videos are the most common speed problems. A single uncompressed photo can easily be 5-10 MB, making your page painfully slow.
Before you upload your images:
- Compress them using tools like TinyPNG
- Use JPEG for photos, PNG for graphics with text
- Try WebP format for even better compression (works on most modern browsers)
- Resize images to the exact size they’ll display (don’t upload 4000px photos to display at 800px)
For videos:
- Host on YouTube or Vimeo instead of your server
- These platforms handle compression, streaming, and bandwidth automatically
- Embed the video rather than hosting the file yourself
After optimization, test your website again with Click Raven’s speed checker to measure improvements.
2. Minifying CSS, JavaScript, and HTML
Code files contain spaces, line breaks, and comments that make them readable for humans but add unnecessary file size that can significantly slow down your webpages.
Minifying removes these extras, reducing file sizes by 20-50% without changing how the code works.
To minify:
- Use plugins if you’re on WordPress (like WP Rocket or Autoptimize)
- Use build tools if you’re a developer (webpack, gulp)
- Use online services for quick one-time minification
Always keep backup copies of your original files before minifying. You’ll need the readable versions if you need to make changes later.
3. Using Content Delivery Networks (CDN)
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) stores copies of your website on servers worldwide.
When someone visits your site, they get content from the server closest to them, dramatically reducing latency and loading time.
How CDNs help:
- Visitors in London load from London servers
- Reduces latency (travel time for data)
- Handles traffic spikes better
Technical Improvements for Speed
Improving website speed involves several technical enhancements. However, these improvements require technical knowledge or help from a developer. If you’re uncomfortable with code, share this section with your web developer or hosting provider.
1. Server Response Time
Your server’s response time (Time to First Byte or TTFB) affects how quickly your page starts loading. Slow server response makes everything else slower, too.
To improve server response:
- Upgrade to better hosting if you’re on cheap shared hosting
- Use server-side caching
- Optimize database queries
- Choose hosting with servers near your audience
2. Database Optimization
If you’re using WordPress or another database-driven CMS, your database can become bloated with revisions, spam comments, and unused data over time.
To clean up your database:
- Delete post revisions
- Remove spam comments
- Clear transient data
- Use plugins like WP-Optimize (for WordPress)
Regular database cleanup can improve speed by 10-20%, especially for older websites.
3. Enable Compression
Most modern hosting providers enable compression by default. Check with your host if you’re unsure. The speed improvement is significant for text-based files like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
Mobile Optimization
More than half of all web traffic now comes from phones and tablets. You lose visitors and rankings if your website doesn’t work well on mobile.
1. Responsive Web Design
Responsive web design ensures that your website adjusts seamlessly to various screen sizes. This approach involves using flexible layouts, images, and CSS media queries to create a site that looks good on any device.
Key features include:
- Text should be readable without zooming
- Buttons should be large enough to tap easily
- Images should resize to fit the screen
- No horizontal scrolling required
Most modern WordPress themes are responsive by default. If your site isn’t responsive, it’s time to update your design.
2. Mobile-First Indexing
Google now primarily uses the mobile version of your website for indexing and ranking. This means your mobile speed is more important than your desktop speed.
To optimize for mobile-first indexing:
- Test your mobile speed using Click Raven’s speed checker
- Ensure all content appears on mobile (don’t hide important content on small screens)
- Make buttons and links easy to tap
- Avoid pop-ups that are hard to close on mobile
Speed Testing Best Practices
To get the most accurate results from your free website speed checker:
1. Test Multiple Times
Run 2-3 tests and use the average. Speed can vary slightly between tests due to server load or network conditions.
2. Test from Relevant Locations
Choose test locations based on your actual audience. Check your analytics to see where most visitors come from, then test from those regions.
3. Test Different Pages
Different pages may have different speed issues, so don’t just test your homepage.
Also check:
- Your most popular blog posts
- Product pages (if e-commerce)
- Landing pages from ads
- Your checkout or signup pages
4. Test Before and After Changes
Establish a baseline score before making changes. Then test again after optimization to measure improvement.
Record:
- Date of test
- Performance score
- Load time
- Page size
- Number of requests
5. Test on Different Devices
Use Click Raven’s speed checker to test desktop performance, but also check mobile speed separately, since mobile is often slower.
6. Compare Against Your Competitors
Test your competitors’ sites to see how you stack up. If they are faster, investigate what they’re doing differently.
7. Schedule Regular Testing
Set a monthly reminder to test your website. Speed can degrade over time as you add content and features.
Test After These Events:
- Installing new plugins or apps
- Changing themes or templates
- Major content updates
- Hosting provider changes
- Adding new integrations
- Site redesigns
8. Act on the Results Quickly
Don’t just test, but fix issues immediately. The longer your site stays slow, the more visitors and revenue you lose.
Conclusion
Website speed directly impacts whether visitors stay on your site or leave. Fast sites keep visitors engaged, convert more customers, and rank higher in search results. This means that slow sites do the opposite.
Luckily, speed issues are fixable, and testing is free with Click Raven’s free website speed checker. Focus on the most significant problems, usually images, scripts, or hosting quality.
Then test regularly to catch problems early. Finally, monitor improvements alongside your search rankings to see how speed optimization helps your visibility.
