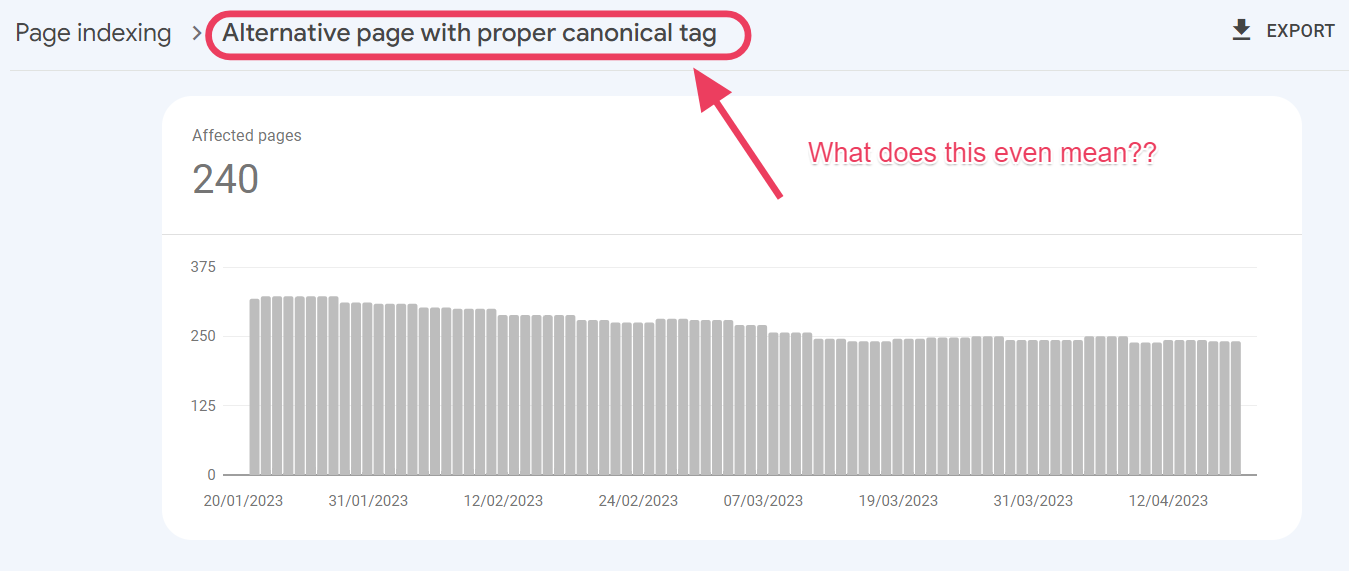
Are you getting the “alternate page with proper canonical tag” message in Google Search Console and wondering what to do with it? In this article, we will discuss this status in further detail so that when you see it on your Google Search Console, you can take the necessary steps to fix the issue.
If you feel this is too much work already, check out our SEO audit service to help you discover why your website has canonicalization errors, among other technical issues.
What Is a Canonical Tag?
A canonical tag is also known as a canonicalized URL, a canonical link, or a rel canonical. A page is tagged on Google Search Console as canonical when there is a duplicate version of it. A canonical tag means that Google has marked the page as the original and indexed it.
What Does “Alternate Page With Proper Canonical Tag” Mean?
In summary, Google is telling you that the pages listed here on this status have alternative duplicate pages, and Google has preferred those duplicate pages for indexing. Therefore, these pages listed here have not been indexed and are not being served on Google.

This means that Google can index alternative pages by inspecting the URLs listed here.
For example, this page is listed under “alternate page with the proper canonical tag.” I clicked on the URL, which gave me a pop-up on the side with some options. I chose to Inspect the URL to find out which page Google serves users instead of this one. In other words, which page is canonicalized?

When inspection of the URL ended, Google showed me below the canonicalized page and the page that it is showing users instead of the one above:

Under the “Indexing” sub-title, Google shows me the indexing page instead of the first URL.
Inspecting the Links in This Scenario
When analyzing these two URLs, I can see that the only difference is the forward slash (/) at the end of the link: URL 1 doesn’t have the forward slash, while URL 2 does.
URL 1: /the-cloud-mvrdv
URL 2: /the-cloud-mvrdv/
When we publish blog posts on this WordPress site, the forward slash is automatically added at the end of every link. The original blog post has the forward-slash (/) at the end. That makes the URL 2 above the original one. It makes sense why Google didn’t pick URL 1 for indexing – it is not the original link.
URL 2 is the alternate page with the proper canonical tag, which is being indexed and served on Google.
This also means that URL 1 is not being served. The message on Google Search Console is that this URL 1 link exists on your site. Even though Google found it, it is a duplicate URL and will not be preferred over URL 2, which is the original version.
Troubleshooting
You might be asking yourself, how in the world did URL 1 without a forward slash exist if all articles automatically publish with a forward slash?
Well, in this case, there is only one scenario why this URL 1 exists. Someone on the site added this link as an internal link on a different blog post but did not add the forward slash at the end of the link. Therefore, when Google crawled the site and came across this link without the forward slash, it became a duplicate version of the original link with a forward slash. Google chose not to index the page without a forward slash and marked the page with the forward slash as the proper canonicalized URL for indexing.
This is just one example of some links in the “alternate page with proper canonical tag” status on the Google search console.
How Do You Fix the ‘Alternate Page With Proper Canonical Tag” Status?
In some cases, you don’t need to fix anything. Why? Google has checked a set of duplicate links and chosen the original version—most likely the one we created first. Google has then added all the other duplicates to this list so that you know it chose the original. Therefore, Google is not indexing these pages listed under this status.
In this case, Google is correct in choosing the original page, so Google is accurate. So you don’t have to do anything.
But what if Google is wrong? In some cases, this happens. Google chooses to index an alternate page from the one listed here, but you want the one listed here to be the right page for indexing.
If that’s the case, then you need a fix.
So what do you do?
1. Set the Correct Canonical URL
These pages under “alternate page with proper canonical tag” are not being indexed because other pages are marked as canonical, and Google is crawling them instead.
Removing the canonical URL and setting the right one on the page under the “alternate page with proper canonical tag” status is the best fix for this issue.
Therefore, you would go to the alternate page that Google is currently indexing and remove the canonicalization. Then, return to the page you want Google to index instead and add the rel canonical in the page header.
Use the simple code below:
<head>
<link rel="canonical" href="https://www.kontely.com/canonical-url/>
</head>2. Check Your Internal Links
In the case we shared in the screenshots above, we need to be careful about adding internal links on this site. This would ensure that the URL 1 without the forward slash would never happen. All my internal links would have the forward slash like URL 2.
I would quickly fix this issue using one of two ways:
- Redirect URL 1 to URL 2 using a 301 redirect
- Audit my internal links to find where URL 1 was added without the forward slash. Fix this by adding a forward slash at the end of that link.
Depending on which is more manageable, both solutions would work just fine.
3. 301 Redirects
I have used a 301 redirect because the page is the same. Only the forward slash creates a scenario where Google thinks these are two duplicate pages.
When using 301 redirects to fix this for your use case, ensure you don’t want to keep the duplicate pages. Once you redirect them, you cannot access the duplicate pages. You might as well delete the pages and implement the redirect.
The redirection plugin for WordPress websites is a quick way to implement the 301 redirect.
Conclusion
We have established that the “alternate page with proper canonical tag” status means the pages listed are not being indexed. Some might be okay, while others need a fix by:
- Telling Google which page to canonicalize and index instead
- Going through our internal URLs to fix poorly done internal links
- Implementing 301 redirects to the right alternate page with proper canonical tags. Inspect the URL to find which links Google is indexing, and then do the 301 redirect to those links.
Remember, if you need us to do a thorough SEO audit of your website, don’t hesitate to contact us. The most common reasons for canonicalization errors are excessive duplication and poor internal linking practices. Today, we can investigate these technical issues by diving deeply into your website.