There has been a rapid increase in AI-powered search experiences like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google’s evolving Search Generative Experience (SGE).
And businesses and content creators are facing a stark reality: ranking well in traditional search results is no longer the sole path to online discoverability.
Leaders must now rethink their content through two distinct, yet interconnected lenses: SEO and GEO.
What is SEO?
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the well-established practice of improving a website’s visibility and ranking in traditional SERPs to drive organic traffic and ultimately, conversions.
Here is a visual example of the traditional SEO ranking system of blue links that direct users to your page.
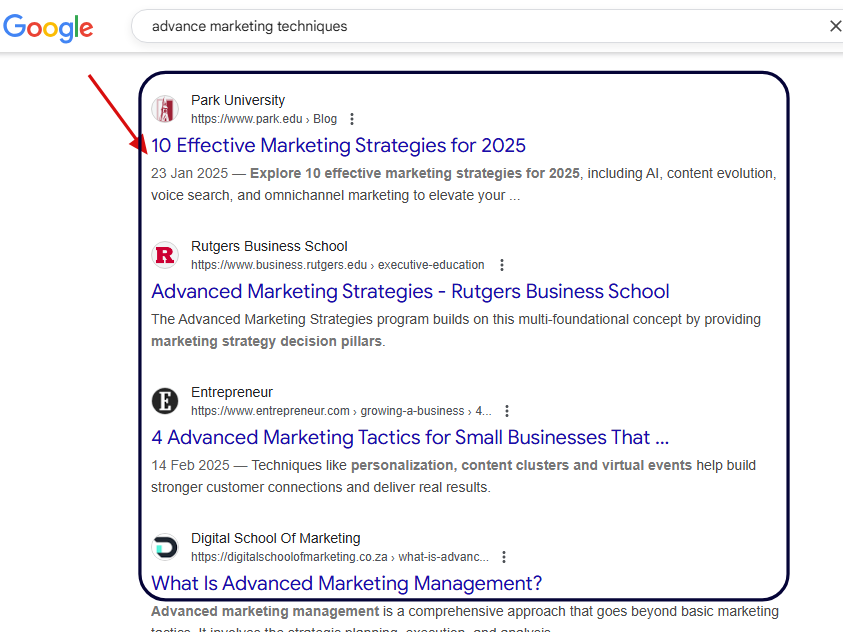
The primary audience for traditional SEO has always been human searchers using platforms like Google, Bing and YouTube.
Its evolution traces back to the early days of the internet, when basic algorithms analyzed keywords to determine relevance.
Over decades, SEO has matured into a complex discipline, built upon these core pillars:
- Technical SEO: Ensuring a website is crawlable, indexable and has a healthy technical foundation (e.g., site speed, mobile-friendliness, structured data implementation).
- On-page SEO: Optimizing individual web pages for specific keywords and user intent (e.g., title tags, meta descriptions, headings, content quality, internal linking).
- Off-page SEO: Building authority and trust through external signals like backlinks from reputable websites, brand mentions, and social signals.
- Content Strategy: Creating authoritative and engaging content that answers user queries and satisfies their needs.
What is GEO?
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is the newer and more nuanced process of making your content retrievable, referenceable and directly cited by AI engines and large language models (LLMs).
Unlike traditional SEO, which aims to get users to click on your link, GEO aims to have your content become the answer, or at least a highly credible source for an AI-generated answer.
To visualise the current AI search, here’s a screenshot that shows an AI overview summary on the left and the relevant cited pages on the right.
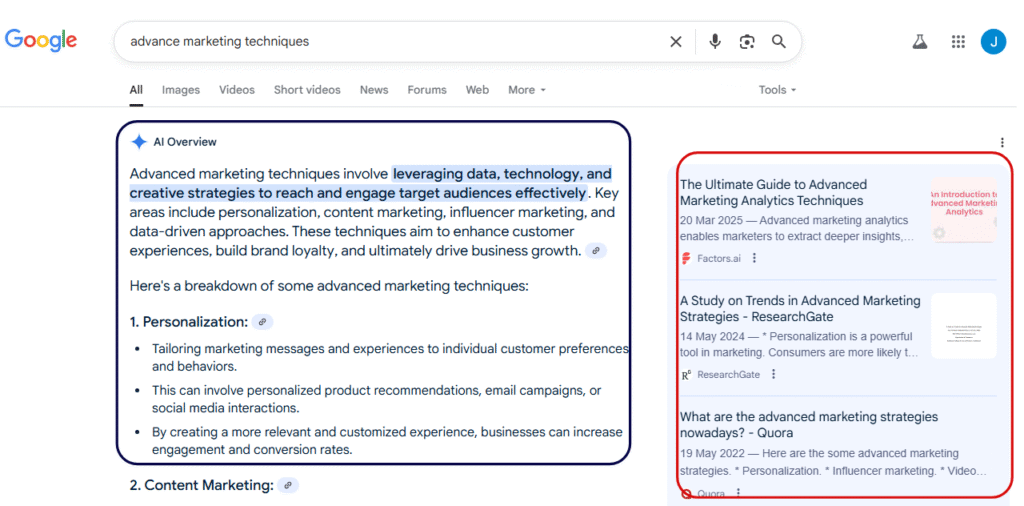
The audience for GEO is fundamentally different: it’s AI models themselves and by extension, the users interacting with AI agents and conversational interfaces.
With GEO, the focus shifts from keywords in isolation to a deeper understanding of structured data, chunked facts, machine-readable formats and pervasive brand mentions.
Key Differences Between SEO and GEO
While both SEO and GEO aim for online visibility; their approaches, targets, and success metrics diverge significantly.
Here’s a breakdown of their core differences:
| Element | SEO | GEO |
| User Intent | Human search queries (e.g., “best running shoes”) | AI prompts, conversational queries, and agent tasks |
| Ranking Mechanism | Indexing + Algorithmic SERP ranking | Retrieval + LLM reasoning and summarization |
| Optimization Target | Search engine crawlers (Googlebot, Bingbot) | Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, Perplexity |
| Format Focus | Optimized webpages, meta tags, links, comprehensive articles | Data chunks, clean facts, structured formats (schema, tables, FAQs) |
| Metrics | Rankings, organic traffic, click-through rate (CTR), conversions | Mentions, citations, direct answers, embeddings, brand visibility within AI responses |
How GEO Impacts the Modern Marketing Funnel
AI assistants fundamentally alter the traditional marketing funnel by introducing a new, critical discovery layer: zero-click discovery.
A study by Wordstream shows that 58% of Google searches now result in zero clicks as consumers bypass traditional search results entirely.
- An example is when I asked an AI assistant: “What are the best noise-canceling headphones for travel?”
Here is a snippet of the response from a list of 10 items ranked by quality:
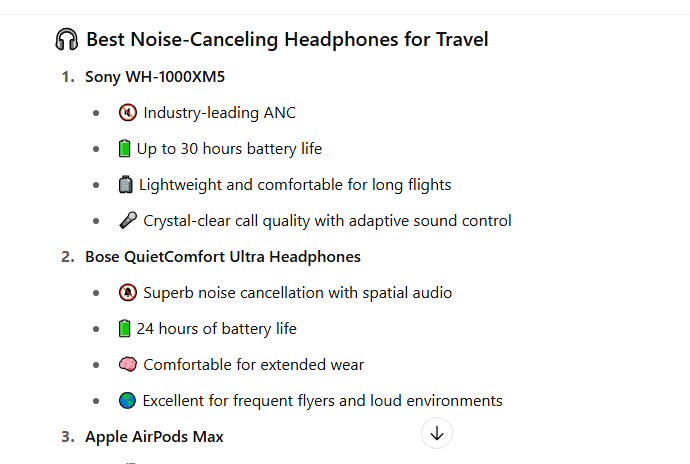
This shows that if your brand’s content isn’t visible to AI or detailed in a way that’s digestible by LLMs, you’re missing a massive chunk of the early-stage consumer journey.
How SEO and GEO Work Together
SEO and GEO are not mutually exclusive. Here is how they complement one another:
- SEO Feeds GEO: Well-structured and optimized content that is easy for crawlers to understand and organize is more likely to be pulled into AI-generated summaries.
- Programmatic Content For Dual-Purpose: Content generated programmatically for SEO scale (e.g., thousands of product variations or location pages) can be designed with GEO in mind to serve traditional search intent and AI prompts.
- Brand Consistency and Trust: Both SEO and GEO benefit immensely from a consistent brand message, strong trust signals (E-E-A-T) and factual clarity.
Practical Steps for Marketing Leaders
Marketing leaders must employ sound strategies to prioritize both SEO and GEO initiatives.
For SEO:
Maintain a Strong Foundation
- Invest in technical SEO and monitor your site health.
- Adopt robust backlink strategy for authority,
- Conduct a meticulous keyword mapping to ensure you’re targeting relevant human queries.
Leverage Programmatic SEO for Scale
Programmatic SEO is an efficient way to create content at scale when used strategically.
Otherwise, you run the risk of creating thin content that does not appeal to user intent.
Companies like Zapier have created thousands of landing pages for each product they integrate with using programmatic methods.
Monitor Traditional SERP Shifts
Continuous monitoring of your site is essential. A Semrush study indicates that AI search visitors could surpass traditional search visitors by early 2028 or sooner.
Keep a close eye on how Google’s AI Overviews and other generative features are impacting your organic clicks using tools like Ahrefs and Semrush.
For GEO:
Structure Content Relentlessly
Break down complex information into easily digestible “fact blocks” that AI can readily identify and utilize.
- Implement JSON-LD schema markup meticulously.
- Use HTML tables, bulleted lists, and clear FAQ sections.
Cultivate Brand Mentions Across Trusted Third-Party Sources
AI models value collective intelligence and established authority.
With strategic PR, you can:
- Secure positive reviews on industry-leading platforms.
- Build a strong network of brand citations on high-authority websites.
Test Your Content’s Visibility in AI Platforms
- Don’t just assume.
- Actively search for your brand, products, and key topics in ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude and Google’s AI Overviews.
- Map out when and how your content is cited (or not cited) by these AI models.
Publish Original Research and Definitive Guides
To stand out, create content that offers:
- Unique insights and perspectives
- Proprietary data
- Definitive answers to complex questions
GEO Tools and Metrics to Track
The measurement landscape for GEO is still in its early stages but rapidly evolving.
Here are some tools to consider:
1. Perplexity Pages / Pro Search
This tool enables SEO professionals to research topics, create comprehensive content pages, and reference their own websites for link building.
2. ChatGPT with Browse
It analyzes existing content to identify optimization opportunities and generates SEO-optimized content by browsing current web data.
When Browse is enabled, observe if ChatGPT directly links to or summarizes your content.
3. LLM Retrieval Simulators
These tools test and simulate how LLMs retrieve and process content for AI-powered search results from your site.
4. AI Visibility Tools
Platforms like Writesonic’s GEO, Profound, Peec AI, and Keyword.com are specifically designed to track brand mentions and visibility within AI-generated responses across various LLMs.
They can help you monitor citation frequency, prominence, and even sentiment.
5. Semantic SEO Tools
These tools analyze entities, topics and relationships (beyond just keywords) to improve AI comprehension.
The metrics to track include:
- The frequency of brand/content citations in AI outputs
- The position of your content within AI-generated summaries
- Sentiment of the AI references
- The types of queries that trigger your content as an AI source
The Future: From SEO Teams to Visibility Teams
The traditional “SEO team” must transition into a broader “AI Visibility Team.”
This requires new skill sets and a reimagined workflow:
- Content Engineers
These professionals are essential for structuring content for machine readability and scalability.
- AI Prompt and Retrieval Optimizers
These are specialists who understand how users phrase queries to AI and how AI models retrieve information, enabling them to fine-tune content for optimal AI response.
- Data Structuring Experts
These professionals are skilled in implementing schema, creating robust content models and ensuring data integrity across complex content systems.
Success will depend on how effectively organizations can structure their knowledge base to be consumed and cited by intelligent agents, not just crawled by traditional search bots.
The Brands That Adapt Win
The future of search is no longer just a list of blue links; it’s a combination of AI summarized answers, intelligent agents and interactive AI interfaces.
While traditional SEO is still essential for driving conversions at the final stage of the customer journey, GEO is rapidly becoming critical at the initial, zero-click discovery phase powered by AI.
Marketing leaders must recognize this shift and invest in both SEO’s foundational principles and GEO’s advanced content structuring to double their rewards; visibility and conversions.
To ignore this, is to risk obsolescence.

